|
Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland.† The prostate is a small, walnut-sized structure that makes up part of a manís reproductive system [5].† |
|
DEFINITION |
|
DIAGNOSIS |
|
Most prostate cancer is discovered through routine screening.† Prostate screening test might include: ∑ Digital rectal exam (DRE) ∑ Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test
†††††††††††† PSA testing combined with DRE helps identify cancers at their earliest stages.† If an abnormality is detected on a DRE or PSA test, your doctor may recommend a test to determine whether you have prostate cancer or not, such as: ∑ Ultrasound ∑ Collecting a sample of prostate tissue
†††††††††††† When a biopsy confirms the presence of cancer, the next step, called grading, is to determine the aggressiveness of the cancer.† The tissue samples are studied under a microscope, where the cancer cells are compared with healthy prostate cells.† As the cancer cells become increasingly different from the healthy cells, the more aggressive and the more likely the cancer will spread quickly.† More aggressive cancer cells have higher grades.† The most common scale used to evaluate the grade of prostate cancer cells is called a Gleason score.† Scoring can range from 2 (nonaggressive cancer) to 10 (very aggressive cancer).
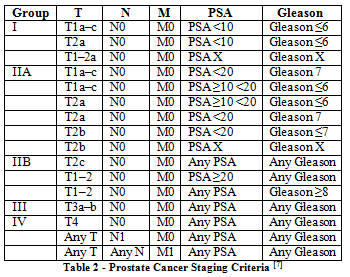
†††††††††††† Once a cancer diagnosis has been made, your doctor works to determine the extent (stage) of the cancer.† If the doctor suspects your cancer may have spread beyond your prostate, imaging tests may be recommended.† Once the testing is complete, your doctor assigns your cancer a stage.† The TNM system is commonly used to stage prostate cancer.† This system evaluates the size of the tumor (T), the extent of involved lymph nodes (N), and any metastasis or distant spread (M).† These are often grouped in four stages, which can be seen in the table below. |
|
Table 1: Stage Description |


Prostate Cancer Decision Support System |
|
GMU Project Class Fall 2011 |
|
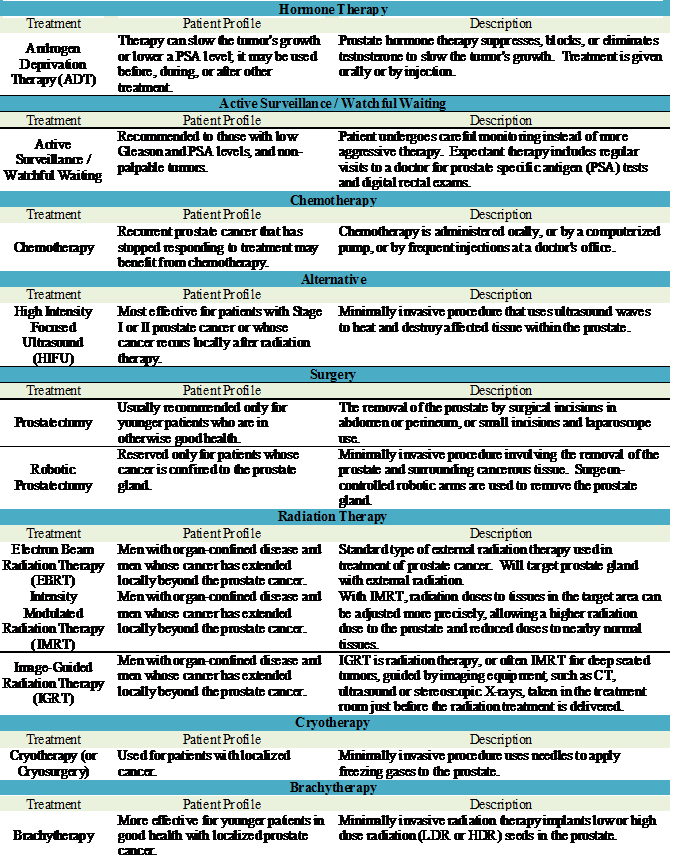
Prostate cancer treatment options depend on several factors, such as how fast your cancer is growing, how much it has spread, your overall health, as well as the benefits and potential side effects of the treatment.† The following treatments are available: |
|
TREATMENTS |
|
Home |
|
Members |
|
Prostate Cancer |
|
Solution |
|
Deliverables |
|
Schedule |
|
DSS Walkthrough |
|
DSS Walkthrough Part II |
|
Works Cited and Links |
|
Home |
|
Members |
|
Prostate Cancer |
|
Solution |
|
Deliverables |
|
Schedule |
|
DSS Walkthrough |
|
DSS Walkthrough Part II |
|
Works Cited and Links |
|
DSS |
|
Prostate Cancer Information |
|
The American Cancer Society estimates that one in every six men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer during his lifetime. The American Cancer Society estimates that one in every six men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer during his lifetime.† More than 2 million men in the United State have been diagnosed with prostate cancer at some point are still alive today[1].†
Prostate cancer is unique in that it is a slow-moving disease.† Quite often a man will die from other natural causes before their prostate cancer has even become noticeable [2].† Because prostate cancer progresses slowly, patients have a variety of treatment options to choose from. There are many factors that play a role in this complex decision.† These factors are driven by the userís health profile (e.g. age or stage of prostate cancer) and preferences (e.g. tolerance of treatment side effects, cost of treatment, etc.). |
|
BACKGROUND |

|
Stage |
Description |
|
I |
Very early cancer thatís confined to a microscopic area that your doctor canít feel |
|
II |
Cancer can be felt, but it remains confined to your prostate gland |
|
III |
Cancer has spread beyond the prostate to the seminal vesicles or other nearby tissues |
|
IV |
Cancer has spread to lymph nodes, bones, lungs, or other organs |